|
||
|
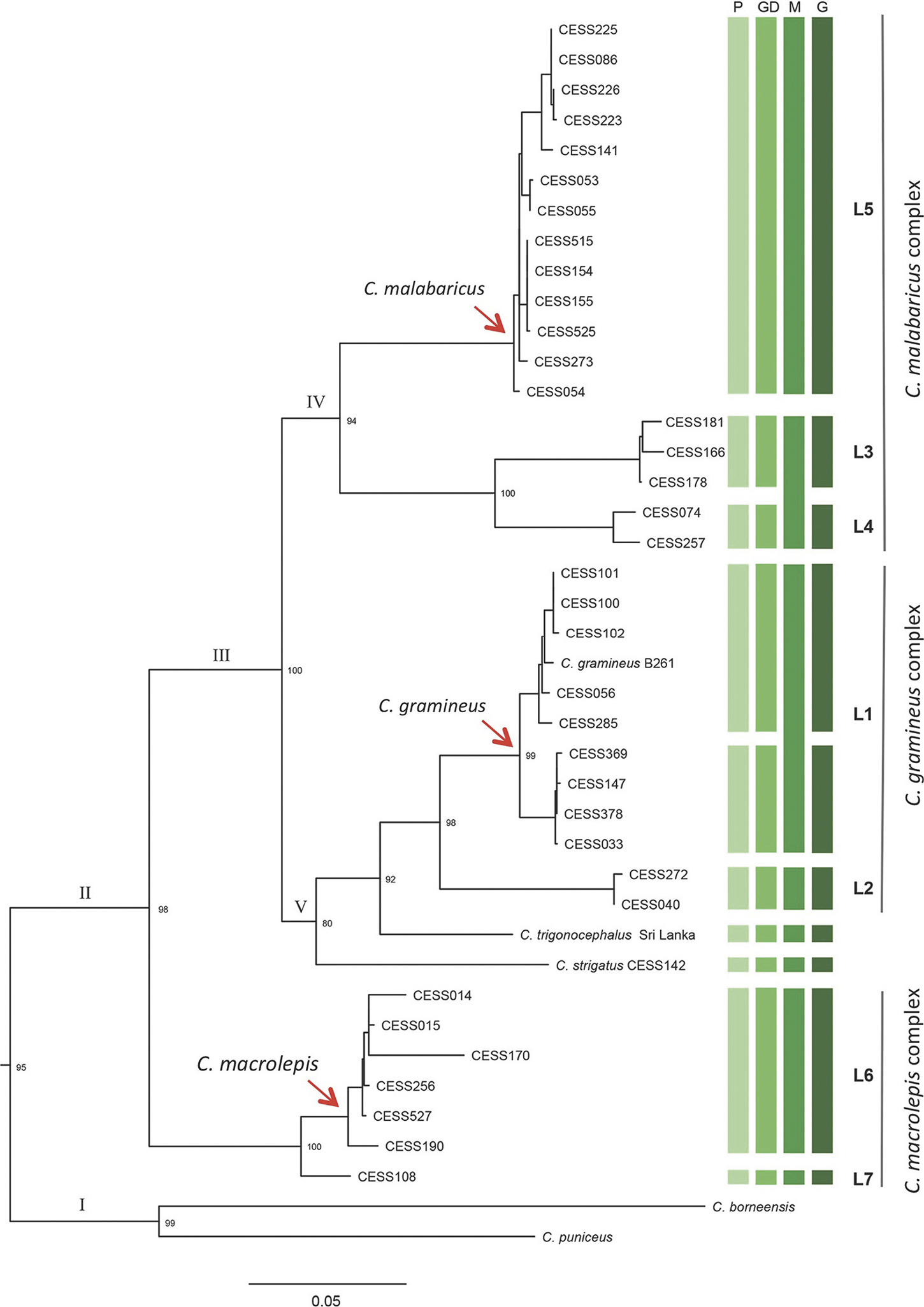
A Maximum Likelihood tree generated from three mitochondrial genes shows the Peninsular Indian, Sri Lankan (I) and Southeast Asian (II) clades. In the Peninsular Indian group (I), the new lineages (L1–L7) are marked with different green bars, which represent the different criteria used to delimit the species boundary. P represents the putative species predicted by bPTP analysis, while GD, M and G represent genetic distance, morphology and geographic isolation. All clades are supported with >70% parametric bootstrap value (see Fig. 1). |